
Jan 30, · A guide to writing the dissertation literature review 1. A peer-reviewed electronic journal. Copyright is retained by the first or sole author, who grants right of first publication to the Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation A quick and easy guide to writing a literature review for your master's Dissertation doctoral dissertation This short guide will give you the How you need write a literature review, no matter what your field of study is. If you're doing your master's or doctoral thesis, you need Literature present a good, detailed literature review in your A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review Justus J. Randolph Walden University Writing a faulty literature review is one of many ways to derail a dissertation. This article summarizes some pivotal information on how to write a high-quali ty dissertation literature review. It begins with a
[PDF] A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review. | Semantic Scholar
Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
See our User Agreement and Privacy Policy. See our Privacy Policy and User Agreement for details. A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review. SlideShare Explore Search You. Submit Search. Home Explore. Successfully reported this slideshow. We use your LinkedIn profile and activity data to personalize ads and to show you more relevant ads.
You can change your ad preferences anytime. A guide to writing the dissertation literature review. Upcoming SlideShare. Like this document? Why not share! Crafting the literature review by Ahmed Hamdy views Literature review Table.
how to wri a guide to writing the dissertation literature review Telenor views Literature Review Worksheet by Sam Landfried views Sample literature a guide to writing the dissertation literature review by cocolatto views Literature Review Review of Relate by Dilip Barad views M-com Previous Year question paper by Education At The Embed Size px.
Start on. Show related SlideShares at end. WordPress Shortcode. EducationTechnology. Like Liked. Education At The Edge. Full Name Comment goes here. Are you sure you want to Yes No. Ku Mohamad Rafiq. Jesús GM at Universidad de Castilla - La Mancha.
No Downloads. Views Total views. Actions Shares. No notes for slide. A guide to writing the dissertation literature review 1. A peer-reviewed electronic journal. Permission is granted to distribute this article for nonprofit, educational purposes if it is copied in its entirety and the journal is credited. Volume 14, Number 13, June ISSN A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review Justus J.
Randolph Walden University Writing a faulty literature review is one of many ways to derail a dissertation. This article summarizes some pivotal information on how a guide to writing the dissertation literature review write a high-quality dissertation literature review.
It begins with a discussion of the purposes of a review, presents taxonomy of literature reviews, and then discusses the steps in conducting a quantitative or qualitative literature review. The article concludes with a discussion of common mistakes and a framework for the self-evaluation of a literature review. Writing a faulty literature review is one of many ways to derail a dissertation. Experienced thesis examiners know this. In a study of the practices of Australian dissertation examiners, Mullins and Kiley found that, Examiners typically started reviewing a dissertation with the expectation that it would pass; but a poorly conceptualized or written literature review often indicated for them that the rest of the dissertation might have problems, a guide to writing the dissertation literature review.
On encountering an inadequate literature review, examiners would proceed to look at the methods of data collection, the analysis, and the conclusions more carefully. Further, dissertations and theses are not the only types of publications that suffer from poor literature reviews. Many literature reviews in manuscripts submitted for publication in journals are also flawed—see Alton-LeeGrante and Graueand LeCompte, Klinger, Campbell, and Menck A guide to writing the dissertation literature review that so many literature reviews are poorly done, it is surprising there is not more published information on how to write a literature review.
Boot and Beile write, Doctoral students seeking advice on how to improve their literature reviews will find little published guidance worth heeding. Most graduate students receive little or no formal training in how to analyze and synthesize the research literature in their field, and they are unlikely to find it elsewhere.
Gall, Borg, and Gall estimate that completion of an acceptable dissertation literature review will take between three and six months of effort.
The purpose of this guide is to collect and summarize the most relevant information on how to write a dissertation literature review. A discussion of common mistakes and a 2. Conducting a literature review also informs the student of the influential researchers and research groups in the field. Apart from the above reasons for writing a review i.
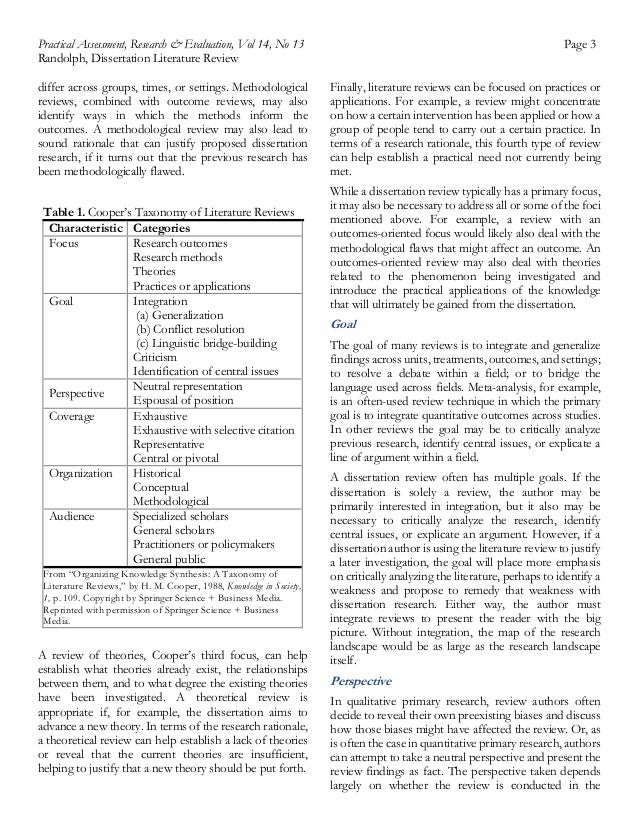
Without establishing the state of the previous research, it is impossible to establish how the new research advances the previous research. As shown in Table 1, Cooper suggests that literature reviews can be classified according to five characteristics: focus, a guide to writing the dissertation literature review, goal, perspective, coverage, organization, and audience.
In Table 1, each characteristic is listed on the left, with the levels of the characteristics on the right. In the paragraphs that follow, each of these literature review characteristics are described in more detail. Focus The first characteristic is the focus of the review. Cooper identifies four potential foci: research outcomes, research methods, theories, or practices or applications.
Literature reviews that focus on research outcomes are perhaps the most common. In fact, the Educational Resources Information Centerp. The Educational Resources Information Center suggests that, in terms of a developing a research rationale, an outcomes-oriented review may help identify a lack of information on a particular research outcome, thus establishing a justifiable need for an outcome study. In a methodological review, research methods in the chosen field are investigated to identify key variables, measures, and methods of analysis and inform outcomes-oriented research.
The methodological review is also helpful to identify methodological strengths and weaknesses in a body of research, and examine how research practices 3. Methodological reviews, combined with outcome reviews, may also identify ways in which the methods inform the outcomes. A methodological review may also lead to sound rationale that can justify proposed dissertation research, if it turns out that the previous research has been methodologically flawed.
Table 1. Cooper,Knowledge in Society, 1, p. A theoretical review is appropriate if, for example, the dissertation aims to advance a new theory.
In terms of the research rationale, a theoretical review can help establish a lack of theories or reveal that the current theories are insufficient, helping to justify that a new theory should be put forth. Page 3 Finally, literature reviews can be focused on practices or applications. For example, a review might concentrate on how a certain intervention has been applied or how a group of people tend to carry out a certain practice.
In terms of a research rationale, this fourth type of review can help establish a practical need not currently being met. While a dissertation review typically has a primary focus, it may also be necessary to address all or some of the foci mentioned above. For example, a review with an outcomes-oriented focus would likely also deal with the methodological flaws that might affect an outcome. An outcomes-oriented review may also deal with theories related to the phenomenon being investigated and introduce the practical applications of the knowledge that will ultimately be gained from the dissertation.
Goal The goal of many reviews is to integrate and generalize findings across units, treatments, outcomes, and settings; to resolve a debate within a field; or to bridge the language used across fields.
Meta-analysis, for example, is an often-used a guide to writing the dissertation literature review technique in which the primary goal is to integrate quantitative outcomes across studies. In other reviews the goal may be to critically analyze previous research, identify central issues, or explicate a line of argument within a field.
A dissertation review often has multiple goals, a guide to writing the dissertation literature review. If the dissertation is solely a review, the author may be primarily interested in integration, but it also may be necessary to critically analyze the research, identify central issues, or explicate an argument. However, if a dissertation author is using the literature review to justify a later investigation, the goal will place more emphasis on critically analyzing the literature, perhaps to identify a weakness and propose to remedy that weakness with dissertation research.
Either way, the author must integrate reviews to present the reader with the big picture. Without integration, the map of the research landscape would be as large as the research landscape itself. Perspective In qualitative primary research, review authors often decide to reveal their own preexisting biases and discuss how those biases might have affected the review.
Or, as is often the case in quantitative primary research, authors can attempt to take a neutral perspective and present the review findings as fact. The perspective taken depends largely on whether the review is conducted in the 4. Since secondary research i. This decision will be dictated by the particular case. Coverage Deciding how wide to cast the net is a critical step in conducting a review. Cooper proposes four coverage scenarios. In an exhaustive review, the reviewer promises to locate and consider every available piece of research on a certain topic, published or unpublished.
However, finding every piece of research could take more time than is available. The key to the exhaustive review is to define the population in such a way that it is bounded and the number of articles to review is manageable. Cooper calls this an exhaustive review with selective citation.
The Structure of a Literature Review - Thesis Writing Guide
, time: 10:14(PDF) A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review | Justus Randolph - blogger.com
A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review Justus J. Randolph Walden University Writing a faulty literature review is one of many ways to derail a dissertation. This article summarizes some pivotal information on how to write a high-quali ty dissertation literature review. It begins with a Mar 03, · The next section of this blog offers 10 top tips on how to ensure you write a great dissertation literature review. 1. Questions Do not begin analysing the literature before clarifying in your own mind the research questions that will guide your dissertation. By formulating problems beforehand, you will avoid wasting hours in aimless reading Apr 22, · A guide for doctoral students to the process of conducting literature searching, analysis, organizing, synthesis and writing a literature review for a dissertation Olga Koz, DM, MLS Associate Professor & Graduate Studies Librarian at the Kennesaw State University
No comments:
Post a Comment